After discussing about comparison between alum and PAC in the last article. This time we would like to discuss about Poly Aluminum Chloride or PCA which is an innovative solution in the world of water treatment. As an efficient coagulant, PAC plays an important role in purifying water and reducing pollution. In Indonesia, the use of PAC has increased along with the awareness of the importance of effective water treatment. Not just for its superior ability to clarify water, PAC is also appreciated for its minimal environmental impact. With better performance over a wide range of turbidity levels and water quality, PAC becomes a more flexible solution than conventional coagulants.
The efficiency of PAC lies not only in its ability to clean water, but also in its economical use. Because PAC is more effective in smaller quantities than other coagulants, operational costs and chemical usage can be reduced, which is especially meaningful for large-scale operations such as those often encountered in Indonesia. In addition, the ease of handling and storage of PAC makes it a practical choice for many water treatment facilities.
PAC has also shown results in reducing the amount of water used for coagulant treatment.
PACs have also shown remarkable results in addressing a wide range of water issues, from reducing turbidity and removing color, to capturing and removing harmful substances such as phosphates, heavy metals, and organic matter. This makes PACs not only important in the context of providing clean water for human consumption, but also in the treatment of industrial effluents, where hygiene and safety standards are very stringent.
In Indonesia, with its diverse range of water supplies for human consumption, PACs have become an essential part of the water supply chain.
In Indonesia, with its diverse water sources and challenges faced in water treatment, PAC offers an adaptive and effective solution. From dense urban areas to remote areas, PACs have been proven to improve water quality, support environmental sustainability, and help ensure access to clean water for more people.

What is Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC)?
PAC is a chemical compound used as a coagulant in water and waste treatment processes. With the chemical formula [Aln(OH)mCl(3n-m)]x, PAC is effective in removing turbidity, color, and other contaminants from water. It is more effective than traditional coagulants such as alum, thanks to its ability to handle a wide range of water conditions.
The advantage of PAC lies in its unique molecular structure, allowing it to work more efficiently in the coagulation process. PAC molecules have a high molecular weight and a strong positive charge, which helps in attracting and binding negative particles suspended in water. This results in larger, heavier flocs that settle more easily, speeding up the water clarification process.
In addition, PACs also have a wider pH application range than traditional coagulants. This means PACs can be used in different types of water with different pHs without the need for additional chemical adjustments. This is particularly beneficial in industrial wastewater treatment, where the quality of incoming water is often diverse.
PACs are also renowned for their effectiveness in treating industrial wastewater.
PAC is also renowned for its effectiveness in reducing heavy metal content and organic substances from water, making it an ideal choice for drinking and industrial water treatment applications. The reduction of heavy metals and organic substances is not only important for human health but is also essential for protecting the environment from pollution.
In the context of sewage treatment, PAC offers advantages in reducing the final effluent load. With its high efficiency in the coagulation process, the amount of sludge produced tends to be lower compared to the use of traditional coagulants. This reduces the cost and complexity in handling and disposing of the effluent, while minimizing the environmental impact.
With all these advantages, it is no surprise that PAC has become a popular choice in water and sewage treatment, both in Indonesia and around the world. With its wide-ranging capabilities in overcoming various water treatment challenges, PAC continues to prove itself as a vital ingredient in the industry.

Use of PACs in Water and Sewage Treatment
PAC is used in various stages of water treatment, ranging from drinking water treatment to industrial effluent treatment. Its effectiveness in binding small particles makes it a top choice in flocculation and sedimentation processes. PACs are also environmentally friendly and safe to use, making them a sustainable choice.
In drinking water treatment, PAC plays an important role in removing organic and inorganic substances that can degrade water quality. This includes removing impurities, reducing turbidity, and decolorizing, which are critical to ensuring the safety and freshness of drinking water. This process not only improves the aesthetic quality of water but also removes contaminants that may be harmful to health.
In the industrial sector, PAC is used to treat effluents that are diverse in composition and contaminant concentration. From mining effluents to pharmaceutical waste, PACs are effective in tackling difficult contaminants, including heavy metals, phosphates, and persistent organic substances. This makes PACs a versatile and indispensable solution in various types of industrial effluent treatment.
PACs also play an important role in domestic wastewater treatment. With the development of urbanization and increase in population, there is a growing need for more effective wastewater treatment methods. PACs help in this process by accelerating the settling of particles, which in turn increases the efficiency of wastewater cleaning.
Environmental sustainability and safety are two other important aspects considered in the use of PACs. Since PACs are more efficient, the dosage required is lower, which means less chemical usage and lower environmental impact. This is especially important in the quest to reduce the industry's carbon footprint and ensure the protection of aquatic ecosystems.
In addition, the ease of handling and application of PAC makes it a practical choice for a wide range of water treatment facilities. Whether for small or large-scale treatment, PACs offer a customizable and efficient approach, meeting the various needs and challenges faced in water and waste treatment.
Advantages of PACs compared to Other Coagulants
One of the main advantages of PAC is its lower dosage compared to other coagulants, yet higher effectiveness. This means that the use of PAC can reduce operational costs in water treatment. In addition, PAC has a wider pH range, making it effective in a wide range of water conditions.
The effectiveness of PAC in lower doses not only saves on chemical costs, but also reduces the burden on the sewage treatment system. By producing a lesser amount of sludge, the costs and complications associated with sewage disposal are significantly reduced. This is a huge advantage, especially in large-scale water treatment operations, where reduced operational and sewage disposal costs can have a substantial economic impact.
In addition, the wide pH range of PACs allows for their use in a variety of water treatment scenarios, from acidic to alkaline water. This means that PAC can be used in more situations without the need for additional pH adjustments, which are often required with other coagulants. This ability makes PACs a very flexible and efficient solution to a wide range of challenges in water treatment.
PACs also stand out for their ability to be used in a wider range of water treatment scenarios.
PACs also stand out for their better ability to remove specific contaminants than conventional coagulants. For example, PACs are highly effective in removing heavy metals, phosphates, and organic substances, which are critical in maintaining drinking water quality and protecting aquatic life. This makes PACs a more effective choice for more specific and sensitive water treatment applications.
PACs' unique ability to remove heavy metals, phosphates, and organic substances, which are critical in maintaining drinking water quality and protecting aquatic life.
PAC's unique ability to treat water with diverse particle content is also a significant advantage. PAC is effective in clarifying water with different levels of turbidity, ranging from highly turbid water to water with low levels of turbidity. This offers greater flexibility in the design and operation of water treatment systems.
Lastly, convenience and simplicity in the use of PAC is also an important factor. PACs are easy to store, handle, and apply, which reduces the need for specialized training and additional equipment. This makes PAC a practical and efficient solution for a wide range of water treatment facilities, both for commercial and industrial use.
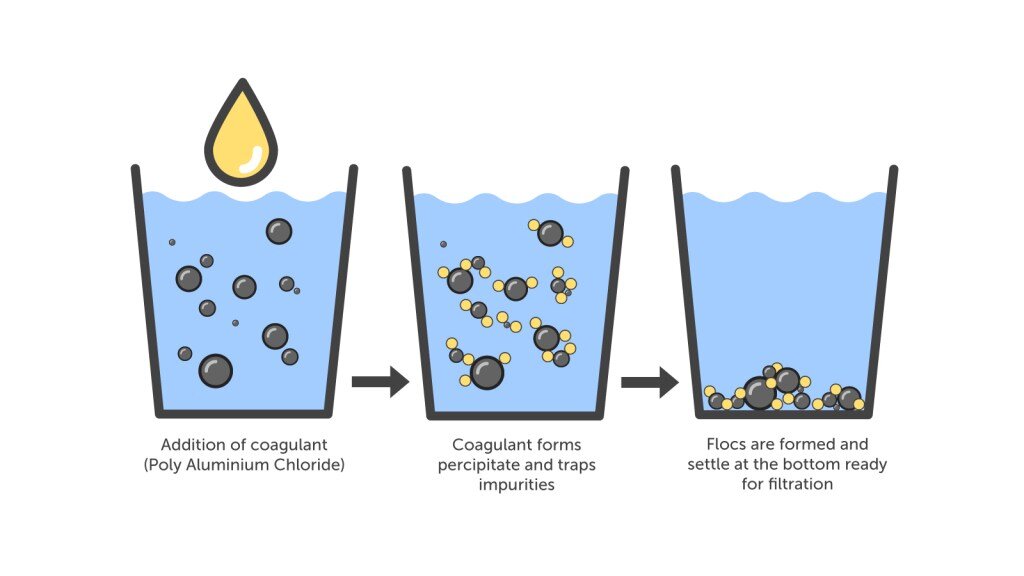
How PAC Works in Water Treatment
PAC works by forming larger and heavier flocs of dirt particles, making them settle easily. This process helps clarify water with high efficiency. The use of PAC also helps to reduce the amount of sludge produced, making it easier to handle the effluent.
The mechanism of action of PAC in clarifying water starts with the coagulation process, where PAC molecules react with small particles suspended in water. These molecules, which are often too small to settle naturally, become bound by the positive charge of the PAC ions. This process transforms the particles into larger flocs, which are easier to settle or filter out of the water.
The resulting flocculation process produced by the PAC ions is the first step in the process.
The flocculation process that PAC produces is highly effective due to the unique molecular structure of PAC. This structure allows PAC to form networks that capture particles more efficiently than with traditional coagulants. As a result, the water clarification process becomes faster and more efficient, resulting in clearer and cleaner water.
In addition to its efficiency in forming flocculation, PACs can also form networks that capture particles more efficiently than traditional coagulants.
In addition to efficiency in forming flocs, PACs also have the advantage of reducing the need for chemical additives. In many cases, the use of PACs reduces or even eliminates the need for pH adjustment chemicals or other chemical additives that are often required in traditional water treatment processes. This not only saves costs but also reduces the complexity of the treatment process.
The effectiveness of PAC in reducing the amount of sludge produced is another important benefit. Less sludge means less effluent that needs to be handled and disposed of, which reduces the operational costs and environmental impact of the water treatment process. This simpler and more efficient waste handling process is invaluable, especially in large-scale water treatment operations.
The use of PACs also provides a significant benefit to the water treatment process.
The use of PACs also provides additional benefits in terms of final water quality. Water that has been treated with PAC often has lower levels of contaminants, including heavy metals and organic substances, which are important for human health and the environment. This makes PACs not only an efficient option but also a safer and healthier option in water treatment.
Considerations in Using PACs
In using PAC, it is necessary to consider the right dosage according to the quality of the water to be treated. Setting the pH is also important to maximize the effectiveness of PAC. In addition, continuous monitoring of the treatment process and results is important to ensure that the resulting water quality meets the set standards.
Determining the correct dosage is key to the quality of the water to be treated.
Determining the right dosage is key in the effective use of PAC. Excessive dosage can cause problems such as increased turbidity due to the formation of too large flocs or excessive chemical usage, which can have a negative impact on the environment. On the other hand, too low a dose may not be effective enough in clarifying the water or removing contaminants. Therefore, it is important to conduct regular trials and dosage adjustments based on the specific characteristics of the water being treated.
PH regulation is another important aspect in the use of PACs. Although PACs are effective in a wide pH range, pH adjustment can be necessary to optimize the coagulation and flocculation process, especially at sites with highly variable water conditions. Keeping the pH at an optimal level not only maximizes the effectiveness of the PAC but also helps reduce the formation of unwanted side compounds.
Continuous monitoring is an important part of the process of using PAC. This includes regular checks of incoming and outgoing water quality, as well as monitoring of the coagulation and flocculation process. This monitoring allows for the rapid identification and treatment of any problems that may arise, as well as any necessary process adjustments to ensure consistency in the quality of the water produced.
In addition, it is also important to ensure the quality of the water produced is consistent.
In addition, it is also important to consider the safety and handling aspects of using PAC. While PAC is generally safe to use, proper handling is required to avoid risks such as skin or eye irritation. Employees working with PACs should be equipped with appropriate safety equipment and trained in safe handling protocols.
Finally, the selection of PAC type is important.
Finally, selection of the right type of PAC is also important. There are different types of PACs in the market, each with different characteristics. Selecting the most suitable type of PAC for a specific application and specific water conditions is a crucial step to ensure the effectiveness of the water treatment process.
Case Study: PAC Usage in Indonesia
In Indonesia, PACs have been used in various water treatment projects, ranging from industrial plants to drinking water treatment plants. For example, the use of PAC in one water treatment plant in West Java significantly improved water quality, while reducing operational costs.
The project involved wastewater treatment.
The project involved the treatment of wastewater from various industrial sources that previously posed serious problems with turbidity and chemical content. The introduction of PAC into the water treatment process helped address these issues effectively. After the implementation of PACs, test results showed significant reductions in turbidity, color, and organic matter content, making the water safe for recycling and reuse in industrial processes.
Furthermore, at a plant, the water was treated with PACs.
Furthermore, at a drinking water treatment plant in another area of Indonesia, PAC was used to address water quality challenges due to variable water flow. Prior to using PAC, the plant often had difficulty managing changes in incoming water quality, especially during the rainy season. However, with proper adjustment of the PAC dosage, they managed to maintain consistent drinking water quality throughout the year, meeting stringent health standards.
The successful application of PAC was also seen in water treatment projects in the mining sector. At one mine site, wastewater containing fine particles and heavy metals was a challenging problem. The use of PACs in the coagulation and flocculation process resulted in a dramatic increase in particle separation efficiency and a reduction in heavy metal content, allowing the wastewater to be managed more safely and efficiently.
The successful use of PAC in various sectors in Indonesia demonstrates its adaptability and effectiveness in addressing various water treatment challenges. This confirms the role of PAC as a vital water treatment solution, not only in the industrial context but also in the provision of clean water for public needs.
Conclusion
Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC) has proven to be an effective solution in water and sewage treatment. With its advantages over other coagulants, PAC offers a more efficient, economical, and environmentally friendly approach. In Indonesia, the use of PAC continues to grow along with the increasing awareness of the importance of quality water treatment.
The effectiveness of PAC in addressing a wide range of water treatment challenges has made it a top choice for many industries and water treatment facilities. From improved drinking water quality to safer and more efficient industrial effluent management, PACs have been key in achieving higher environmental standards and ensuring clean water availability.
We at Beta Pramesti Asia understand the importance of innovation and quality in water treatment. Therefore, we are proud to have our own production PAC plant with a capacity of 20,000 tons per year, which enables us to provide high-quality and consistent PAC solutions for your water treatment needs. With this production capacity, we are committed to meet the growing demand and support water treatment projects across Indonesia.
Contact us via E-mail or Whatsapp for more information about PAC water treatment solutions. Discover a range of innovative and effective water treatment solutions from Beta Pramesti Asia to meet your specific needs. With our experience and expertise, we are ready to help you achieve optimal water treatment standards.
